
GC/MS Off-Flavor Analyzer
Solving odor problems requires identifying the substances causing the odor. However, accurate identification requires relevant knowledge, such as knowing which types of compounds can cause odors, the odor quality, and threshold levels for sensing odors. This system combines a database of the major odor-causing substances and associated sensory information with a GC-MS. It provides a total solution necessary for analyzing odors.
Product Description
Solving odor problems requires identifying the substances causing the odor. However, accurate identification requires relevant knowledge, such as knowing which types of compounds can cause odors, the odor quality, and threshold levels for sensing odors. This system combines a database of the major odor-causing substances and associated sensory information with a GC-MS. It provides a total solution necessary for analyzing odors.
Technical specifications
All Odor-Causing Substances Identified from Previous Problems Are Registered.
The database includes information registered about all odor-causing substances identified from previous problems. Therefore, even if you don't know what types of compounds can cause odors, this database allows you to start analyzing them immediately.
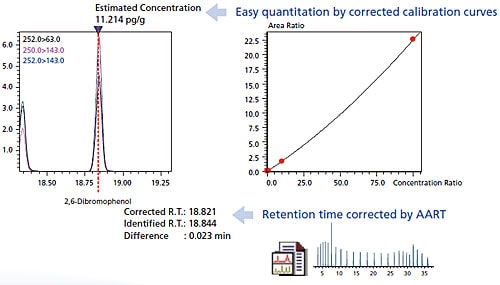
Accurate Identification and Easy Quantitation Are Possible Even Without Standard Samples.
Retention indices for each odor component are registered in the database. The AART function can be used to accurately identify components registered in the database by calculating their retention time using retention indices for substances with a wide range of boiling points. In addition, concentrations can be quantified easily based on the calibration curve information registered in the database.
Substances Causing Odors Can Be Identified Based on Odor Characteristics and Odor Threshold Values.
Sensory information about odor components (characteristics and threshold values) is registered in the database. Therefore, by comparing the concentration of components identified in chromatograms with the threshold values, the substances causing odors can be identified. Furthermore, odor components can also be identified by actually smelling them using a sniffer unit.
Analytical System for Reliably Identifying Odor-Causing Substances
Process Flow Using the GC-MS Off-Flavor Analyzer
Three Different Types of Columns Can Be Selected for Detecting a Wide Variety of Components with High Sensitivity.
Odors Can Be Confirmed Efficiently Using Predicted Retention Time Display Function.
On systems with a sniffer unit, odor components identified from the database can be confirmed. The system includes a function that displays estimated retention times for detected components, so that they can be confirmed based on time.